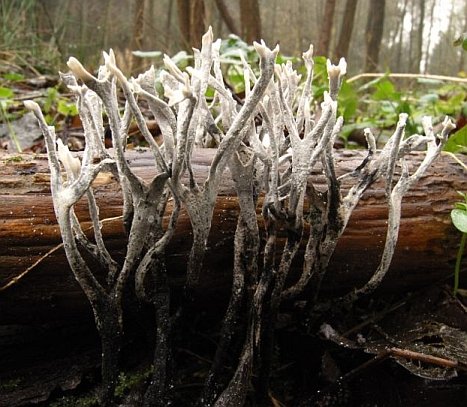
The candlesnuff fungus, Xylaria hypoxylon (L.) Grev.
Synonyms
Clavaria hypoxylon L., Sp. Plantarum: 1182 (1753)
Sphaeria hypoxylon (L.) Pers., (1796)
Xylosphaera hypoxylon (L.) Dumort., (1822)
Common names
Candlesnuff fungus
Carbon antlers
Stag horn’s fungus
Geweihförmige Holzkeule (German)
Xylaire du bois (French)
Description
Fruiting body: erect, tough, rubbery, club-shaped (clavaroid) in shape, usually branched near the top, up to 6 cm high by 3-5 mm wide, often flattened in cross section above, rounded below; the base dark brown to black, often tomentose, branch tips white from asexual spores (conidia) or the same color throughout as the base and minutely pimpled with perithecial pores.
Spores: ascospores are 10-14 X 4-6 µm, black, smooth, bean-shaped. Asexual spores hyaline, smooth, elliptical to elongated.
Habitat: Scattered to gregarious to clustered on rotting wood.
Chemical test: the asci tips stain blue with Melzer’s reagent.
When found in spring, these interesting saprobes are sometime dusted with ascospores, which may look like whitish-grey powder. A jolt will release these spores, to be carried away by air currents – hence the common name candlesnuff fungus.

My name is Austin Collins.
I've dedicated my life to Mushrooms.
I believe Mushrooms are the best kept secret when it comes to health and well being.
For that reason, I would like to share a company with you that in my opinion makes the best mushroom products on the market.
The company is called Noomadic Herbals, my favorite supplement they make is called "Mushroom Total".
I take their products every day and they have helped me think better and have more energy. Give them a try.
-Austin
Bioactive compounds
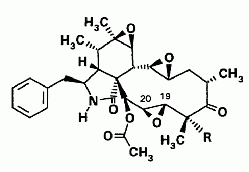
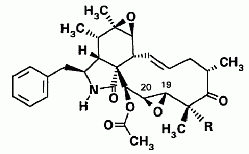
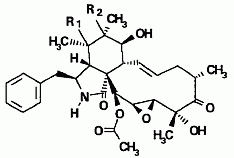
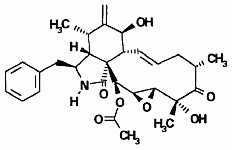
Cytochalasins are organic molecules that bind to actin, a protein component of muscle tissue. Six new cytochalasins (shown below) together with the previously known compounds cytochalasins Q, 19,20-epoxy Q and R were isolated from the fermentation broth of Xylaria hypoxylon (Espada et al., 1997).
A)
B)
C)
D)
Cytochalasins in X. hypoxylon. (a) When R=OH, the scientific name is 21-acetoxy-6,7,13,14,19,20- triepoxy-18-hydroxy-16,18-dimethyl-10-phenyl[11]cytochalas-l,17-dion, or 19,20-epoxycytochalasin R. When R=H, it’s 18-deoxy-19,20-epoxycytochalasin R. If there’s a double bond between carbons 19 and 20 and the R-group is OH, the cytochalasin is cytochalasin R.
(b) In this structure the C13-C14 epoxy moiety is replaced with a double bond. Here, when R=OH, it’s called 19,20-epoxycytochalasin Q, when R=H the molecule is named 18-deoxy-19,20-epoxycytochalasin Q, and if there’s a double bond between carbons 19 and 20 and R=OH, it’s cytochalasin Q.
(c) If R1 and R2 represent an epoxide bond, the compound is 19,20-epoxycytochalasin N; if instead R1 and R2 are replaced with a double bond between carbons 5 and 6, it’s 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C.
(d) This compound is 19,20-epoxycytochalasin D, or 21-acetylengleromycin. Using a variety of spectroscopic methods as well as single crystal X-ray diffraction, the chemical structure was later revised to be 19(βH), 20(αH)-epoxycytochalasin D (Shi and Zhan, 2007).
Two new α-pyrone derivatives, xylarone and 8,9-dehydroxylarone, possessing cytotoxic activities, were isolated from the culture fluid of submerged cultures of Xylaria hypoxylon. The cytotoxic activities of these compounds were also tested in vitro (Schuffler et al., 2007).
Medicinal Properties
Antiviral activity
Polysaccharides extracted from dried fruit bodies of X. hypoxylon using hot water and alcohol precipitation were tested for inhibitory activity against HIV-reverse transcriptase by the colorimetric estimation method (using ELISA). The inhibitory activity of polysaccharides from X. hypoxylon at 1 mg/ml was 80.4 ± 1.2% (Liu et al., 2004).
The compound 19(βH), 20(αH)-epoxycytochalasin D (shown above) demonstrated potent cytotoxic activity against tumor cell line P-388 (Shi and Zhan, 2007). Additionally, a xylose-specific lectin isolated from the candlesnuff fungus showed antiproliferative and antitumor properties. This 28.8 kDa lectin has little amino acid sequence similarity to lectins from other ascomycete mushroom species such as Aspergillus oryzae or Aleuria aurantia. It also has unique carbohydrate-binding specificities, with a potent FeCl3 concentration-dependent hemagglutination property that was inhibited by xylose and inulin. The lectin’s antiproliferative properties towards tumor cell lines M1 and HepG2 was potent, with an IC50 <1µM (Liu et al., 2006).
Links
The exotic look of this species make it a popular subject for nature photographers, and there are quite a few nice examples that can be found on the internet. I’ll just point to a few galleries I found:
- The Czech Biolib site has a gallery.
References
Espada A, RiveraSagredo A, delaFuente JM, HuesoRodriguez JA, Elson SW.
New cytochalasins from the fungus Xylaria hypoxylon.
Tetrahedron. 1997 53(18):6485-92.
Gueguen F.
The morphology and biology of Xylaria hypoxylon L.
Comptes Rendus Des Seances De La Societe De Biologie Et De Ses Filiales. 1906 61:316-7 Part 2.
Liu Q, Luo Q, Feng K, Wang H.
Inhibitory effects of polysaccharide-compound from Xylaria hypoxylon, Agrocybe cylindracea and Trametes suaveolens against HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)-reverse transcriptase.
Edible Fungi of China. 2004 23(4):29-30.
Liu Q, Wang H, Ng TB.
First report of a xylose-specific lectin with potent hemagglutinating, antiproliferative and anti-mitogenic activities from a wild ascomycete mushroom.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 1760(12):1914-9.
Schuffler A, Sterner O, Anke H.
Cytotoxic α-pyrones from Xylaria hypoxylon.
Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung. Section C, Biosciences. 2007 62(3/4):169-72.
Shi LM, Zhan ZJ.
Structural revision of 19, 20-epoxycytochalasin D and its cytotoxic activity.
J. Chem. Res.-S. 2007 3:144-5.
Abstract from IngentaConnect




